After 4 Minutes of Rescue Breathing No Pulse Is Present
Administer one breath every 3 to 5 seconds not exceeding 12 to 20 breaths per minute. If the person is an infant or child age 1 to puberty and he or she is not breathing do chest compressions and rescue breathing for 2 minutes 5 cycles of 30 compressions and 2 rescue breaths then call 911.
1 The process includes opening the patients airway and blowing air into the lungs.
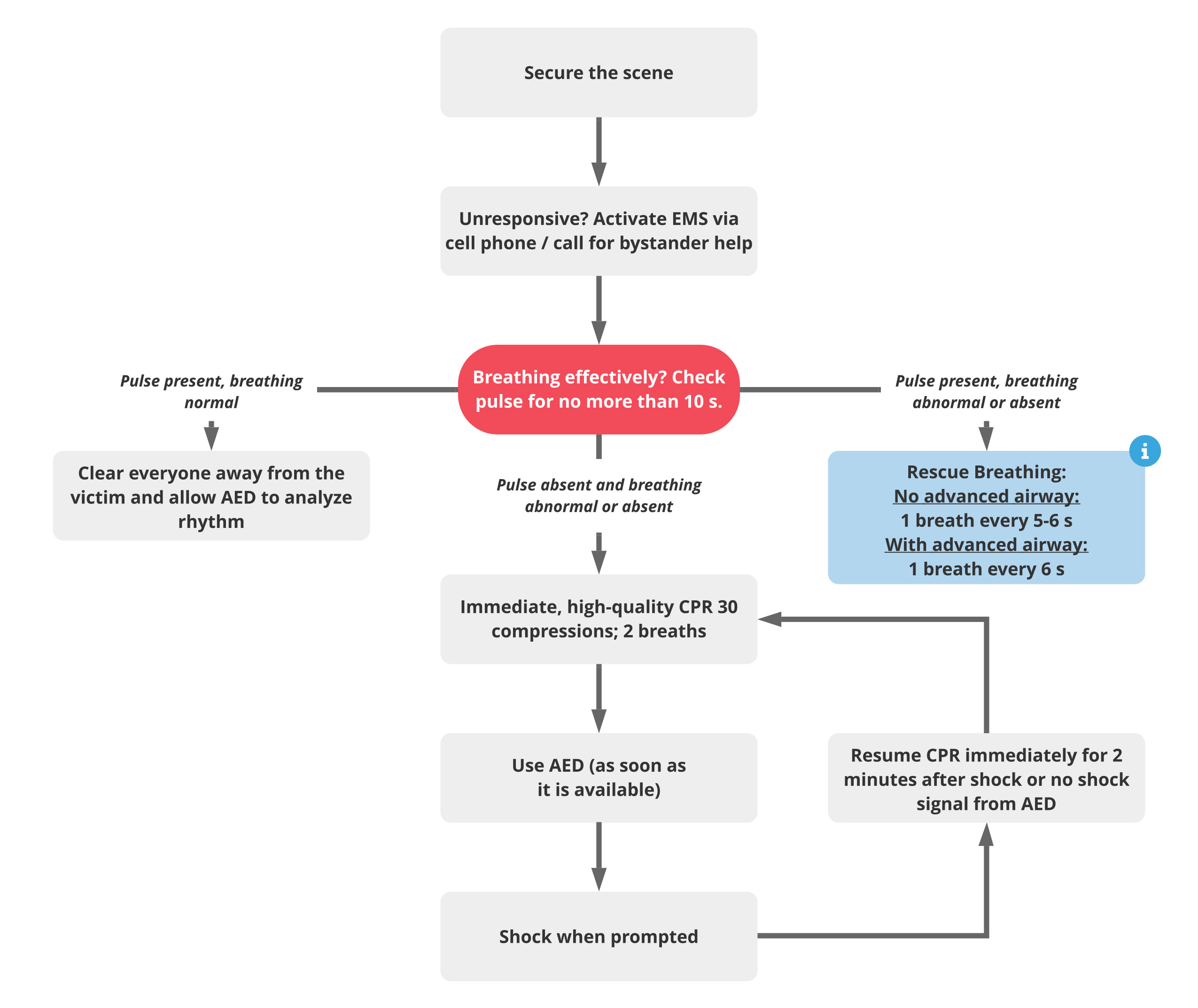
. Ewy and colleagues found that when simulated bystander resuscitation was initiated 4 to 6 minutes after the onset of VF arrest. 1 breath every 5-6 seconds. If not DO NOT STOP.
Place your mouth over the persons mouth making a tight seal. Every 2 to 3 seconds. 2 It sounds simple but opening the airway can be tricky.
If at any point there is no pulse present begin administering CPR. If any of the above things happen then you should or can stop. It still the child is not breathing retilt the head and breathe again.
If the pulse is not present begin CPR. If no normal breathing but pulse present follow the steps below. If the patient definitely has a pulse but is not breathing adequately provide ventilations without compressions.
To effectively give rescue breaths its essential that the persons airway is open and clear. Add compressions if the pulse is less than or equal to 60 beats per minutes with signs of poor perfusion. Push down 15 times.
Breathe into the persons mouth with a firm but a steady breath to make the chest rise. If you still detect a pulse but the patient isnt breathing normally continue with one rescue breath every six seconds for two more minutes. Check for chest rise and breathing.
Chest compressions are done and breaths if given alternate 30 compressions then 2 breaths. Youre going to continue to perform one rescue breath every six seconds for two minutes. Immediately begin CPR and turn on the AED.
Give one breath every 6 seconds. After 15 compressions give the victim two breaths. If the victim has a pulse but is breathing abnormally maintain the patients airway and begin rescue breathing.
After 2 minutes of rescue breathing activate the emergency. For adults you will do 1 breath every 5 seconds and for children and infants every 3 second. 20 to 30 breaths per minute.
This is also called rescue breathing Adults. If the victim is still not breathing begin chest compressions. Check the patients pulse every 2 minutes.
Give the first rescue breath lasting one second and watch to see if the chest rises. At that time reassess the patient. If normal breathing and pulse definitely present monitor until additional help arrives.
Traditional steps during cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR include rescue breathing. Place mask on victims face use bridge of nose to guide. Seal the mask against face index thumb on top other thumb on bottom.
If the victim begins to breathe on his or her own. If a pulse is present one rescue breath should be given every 6 seconds and the pulse rechecked every 2 minutes. 10 to 12 breaths per minute.
To open a persons. Learn about our editorial process. Open the airway using the head-tilt chin-lift maneuver.
You should compress the chest about two inches. Once you are sure that the airway is clear pinch the persons nostrils with your thumb and first finger. Place remaining fingers from second hand on jaw open airway.
Position yourself at victims side. Check pulse and begin CPR if necessary. If it rises give the second breath.
The heart will continue its uncoordinated twitching until it is no longer receiving electrical impulses from the brain and thus stops all together or until the heart is shocked back. That means 40 breaths for children in 2 minutes and 24 for adults every 2 minutes. Brain cells begin to die after 4-6 minutes of oxygen deprivation.
If there is no sign of breathing or pulse begin CPR starting with compressions. Give 1 breath every 5 to 6 seconds. Sometimes the first rescue breath given during CPR doesnt make the chest rise.
Once the heart has stopped it is generally accepted that it takes 4-6 minutes for cerebral biological death to begin and that is temperature dependent. An untrained lay rescuer should provide chest compressions only and not initiate rescue breathing. If at any point there is no pulse present begin administering CPR.
Peter Muller Getty Images. Each breath should last one second. CPR withwithout giving breaths is used when the victim is Unresponsive Not breathing and has no pulse.
Administer one breath every 5 to 6 seconds not exceeding 10 to 12 breaths per minute. At that time reassess the patient. If the child is not breathing do abdominal thrusts.
Pinch the nostrils shut for mouth-to-mouth breathing and cover the persons mouth with yours making a seal. Place your hands in the middle of the victims chest directly between his nipples. The pulse presentno breathing situation has the greatest odds at survival since the heart is still beating.
After four cycles of breaths and compressions recheck for signs of. What immediate action should be taken. Check the patients pulse every 2 minutes.
Give 1 breath every 3 to 5 seconds. Rescue breathing is used when an adult child or infant has a. You do this for 2 minutes and check for a pulse again.
Assess for no breathing or only gasping and check pulse for less than 10 seconds simultaneously. After 4 minutes of rescue breathing no pulse is present during a pulse check. Push fast at least 100-120 compressions per minute.
Act quickly because brain damage can occur after only 3 minutes without oxygen. When to stop rescue breathing. After one minute of rescue breathing continue rescue breathing and checking the pulse each minute.

Bls Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Multi Rescuer Acls Com Resources

Aha 2015 Algorithms For Bls Acls Pals Acls Basic Life Support Algorithm


Comments
Post a Comment